
It is a less common type of port forwarding.ĭynamic port forwarding: The connections from various programs are forwarded via the SSH client, then via the SSH server, and finally to several destination servers. For example, you could connect from your SSH server to a computer on your company's intranet. Remote port forwarding lets you connect from the remote SSH server to another server. Remote port forwarding: The connections from the SSH server are forwarded via the SSH client, then to a destination server. It is the most used type of port forwarding.
For example, you could use the local port forwarding to bypass a company firewall to connect to your client. Local port forwarding lets you connect from your local computer to another server. There are three ways to create an SSH tunnel: Local port forwarding: The connections from the SSH client are forwarded via the SSH server, then to a destination server. SSH tunnels also provide a means to bypass firewalls that prohibit or filter certain internet services. It could also be useful when connecting a client through an SSH server protected by a firewall. The SSH Tunnel can be used to establish a form of a virtual private network (VPN), and since the connection is encrypted, it can be useful for transferring unencrypted traffic over a network through an encrypted channel.įor example, we can use an SSH Tunnel to securely transfer files between a FTP server and a client even though the FTP protocol itself is not encrypted. It’s basically an encrypted tunnel created through an SSH protocol connection. Some people call this device a Jump or server. SSH tunneling is used to create a secure connection between a local and a remote computer, by going through another device that relays a specific service. What does it do exactly? When do you need it? What does it eat in winter? How do you actually set it up? Let’s take a deeper look at it! Which allows to your access services running on remote system or network via SSH network, where you don’t have directly access via port.We often receive questions about our SSH Tunnel entry.

UBUNTU SSH TUNNEL MANAGER WINDOWS
This tutorial helped you to setup local and remote SSH tunnel via the Putty application on Windows server. Next, In the Destination field, enter the destination address followed by the port number.In the Source port field, enter the port number to use on your local system.Select Remote to define the type of SSH port forward.Remote forwarding represents an inversion of the local forwarding process as described above. The Remote forwarding allows a remote system to access resources from your local machine. The tunnel will work until the SSH session is active

Connect the SSH session to make the tunnel. Verify the details you added and press Add button.Select Local to define the type of SSH port forward.Navigate to the Connection > SSH > Tunnels. In the left sidebar under the Category options.Make sure the connection type is set to SSH.Īdd hostname of the SSH server you want to access remotely. In the Session windows, enter the hostname or IP address and port number of the destination SSH server. Start the PuTTY application on your desktop.You can configure local SSH tunneling using the following steps: You can also reverse the process and access resources of your local system from remote machine. The first option shows you option to forward your local port to remote network to access there resources. The Tunnel provides you port forwarding from both sides. Once you forwarded your localhost port to the port listening on remote network, you can directly access the the remote service by accessing configured port with localhost. With the help of SSH tunnel you can access resources available on other ports, which is not directly accessible from your system.
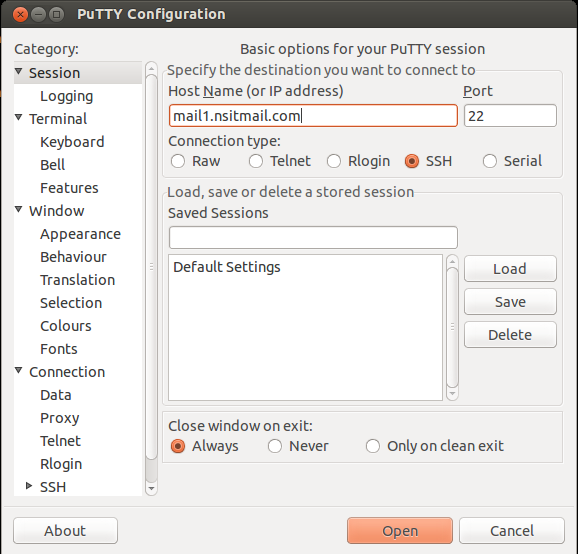
It also provides you option to create SSH tunnel to provide access to resource within the trusted internal network. Most of the Linux system users are aware and use to connect remote system running SSH server. PuTTy is a user-friendly SSH client for the Windows system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
